Business Continuity is the ability of a business to continue its operations with minimal disruption or downtime in the advent of natural or intentional disasters. BC begins with a plan that addresses all risks and secures systems that are vital to business operations.
 A BCP must factor in all the risks, and should ensure continued availability, reliability, and recoverability of resources. It should balance the costs of risk management with the opportunity cost of not taking appropriate action.
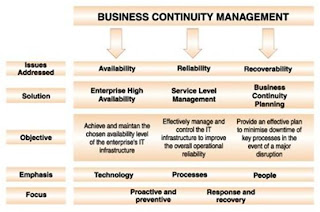
A BCP must factor in all the risks, and should ensure continued availability, reliability, and recoverability of resources. It should balance the costs of risk management with the opportunity cost of not taking appropriate action.A business continuity plan should provide an enterprise-wide risk-based approach, covering People, Processes, Technology and Extended Enterprise to ensure continuing availability of business support systems and minimize disruption risks.
Most corporate today outsource support functions and rely on third-party support for non-core business operations (like logistics). So the plan should also extend to external entities like customers, partners and suppliers. BCP must also address business risks like:
* Customer end risks
* Supplier end risks
* IT hardware and software risks
* Business core process risks
* Business partner risks
* Analysis
* Solution design
* Implementation
* Testing and organization acceptance
* Maintenance
Impact analysis (Business Impact Analysis, BIA)
An impact analysis results in the differentiation between critical (urgent) and non-critical (non-urgent) organization functions/ activities. A function may be considered critical if the implications for stakeholders of damage to the organization resulting are regarded as unacceptable. For each critical function, two values are then assigned:
* Recovery Point Objective (RPO)- the acceptable latency of data that will be recovered
* Recovery Time Objective (RTO) - the acceptable amount of time to restore the function
Solution design
The goal of the solution design phase is to identify the most cost effective disaster recovery solution that meets two main requirements from the impact analysis stage
Implementation
The implementation phase is execution of the design elements identified in the solution design phase. Work package testing may take place during the implementation of the solution.
Testing and organizational acceptance
The purpose of testing is to achieve organizational acceptance that the business continuity solution satisfies the organization's recovery requirements. Testing can include crisis command team call-out testing, technical swing test from primary to secondary work locations, technical swing test from secondary to primary work locations, application test and business process test.
Maintenance
Maintenance of a BCP manual is broken down into three periodic activities. The first activity is the confirmation of information in the manual; roll out to ALL staff for awareness and specific training for individuals whose roles are identified as critical in response and recovery. The second activity is the testing and verification of technical solutions established for recovery operations. The third activity is the testing and verification of documented organization recovery procedures. A biannual or annual maintenance cycle is typical.
CURRENT STATE
The Information Risk Management (IRM) practice of KPMG-India recently conducted a survey to check the preparedness of Indian industry. The results of the survey were shocking:
* 79 percent of the respondents do not have a documented and tested BCM (Business Continuity Management) plan.
* Among the respondents highly dependent on IT, 64 percent do not have a corporate-wide BCM plan in place to address business disruption risks.
The survey covers more than 100 private and public sector organizations spread across various industry segments. (See box on page 26 for a snapshot of the survey results).
A Gartner Research report titled 'What is Crisis Management' indicates something similar. Gartner says only 15 percent of Global 2000 enterprises have a full-fledged business continuity plan.
EXAMPLE FROM INDIA-WIPRO

Sources
1. http://www.publicsafety.gc.ca/prg/em/gds/bcp-eng.aspx
2. http://www.firstsource.com/differentiators/Business-Continuity-Planning.aspx
3. http://www.wipro.com/investors/pdf_files/Wipro_Business_Continuity.pdf
4. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Business_continuity_planning
5. http://howe.stevens.edu/Research/ATT/ReportAllSep1004_v3.pdf
6. http://nonprofitrisk.org/tutorials/bcp_tutorial/intro/1.htm
1 comment:
Thanks for sharing this, it is very important that businesses know this information. Each one should have a business continuity plan that can guarantee the longevity of their company. It is something that businesses should not take for granted.
Post a Comment